Integrated Sciences in Life, Health, and Disease
Studying life in all its facets, translating research into answers on pressing medical, environmental, or social challenges: In order to achieve this objective, researchers at UR’s Faculties of Biology and Pre-Clinical Medicine, Medicine (external link, opens in a new window), and Chemistry and Pharmacy (external link, opens in a new window), rely on synergies while enabling multidisciplinary collaborations within faculties, across departments, and with colleagues in clinical settings or the newly established Faculty of Informatics and Data Sciences. Appropriate structures, such as the Department for Immunomedicine, provide the scholars with excellent transdisciplinary opportunities.
 Graphics © Astrid Riege
Graphics © Astrid Riege Improving medical care by developing highly innovative cell therapeutics for a wide variety of diseases is among the objectives of the Leibniz Institute for Immunotherapy – LIT(external link, opens in a new window) (external link, opens in a new window). Its members, holding chairs and professorships at UR, develop new immune cell therapies for the treatment of diseases with deregulated immune function, such as cancer, autoimmune diseases, or chronic inflammation as well as for the prevention and treatment of transplantation complications.
Research into metastatic tumor disease, the development of diagnostics and pharmaceuticals is at the focus of Fraunhofer ITEM(external link, opens in a new window) (external link, opens in a new window) in Regensburg: Its researchers aim to understand a patient’s individual condition, establish appropriate diagnostics, advance prevention, and optimize therapies. The currently constructed large-scale research building CITO – the Center for Immunomedicine in Transplantation and Oncology – will be equipped with top-notch technological core facilities.
Impressive New Insights

- into fundamental molecular processes inside the cell,
- mechanisms of metastasis formation,
- immune responses upon allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation,
- the interplay of tubular epithelia and interstitial cells of the kidney and the development of innovative therapeutic methods and tools
have been advanced by several DFG-funded Collaborative Research Centers/Transregios (CRC/TRR) coordinated at UR.
Exceptional Research @UR
CRC/TRR 305: Striking a moving target
The CRC/TRR 305 Striking a moving target (external link, opens in a new window): From mechanisms of metastatic organ colonization to novel systemic therapies investigates tumor progression and metastatic colonization dynamic processes.
What kind of genetic, epigenetic and functional armament do disseminated cancer cells use?
Answers provided to those questions are supporting the development of novel adjuvant therapies to prevent early metastatic colony formation and to eradicate candidate metastasis founders.
CRC/TRR 221: Modulation of graft-versus-host and graft-versus-leukemia immune responses after allogeneic stem cell transplantation
Allogeneic hematopoietic stem-cell transplantation is a curative treatment option for patients with high-risk leukemia and lymphoma and for some inherited or acquired hematopoietic deficiencies.
Scientists of the CRC/TRR 221 Modulation of graft-versus-host and graft-versus-leukemia immune responses after allogeneic stem cell transplantation (external link, opens in a new window) develop and investigate innovative immune modulation strategies in order to enhance the safety and efficacy of life-saving stem-cell transplantation in the future.
CRC/TRR 374: Tubule System and Interstitium of the Kidney: (Patho-) Physiology and Crosstalk
The CRC/TRR 374 Tubule System and Interstitium of the Kidney: (Patho-) Physiology and Crosstalk is focusing on chronic kidney disease by investigating the diverse functions and interplay of tubular epithelia and interstitial cells.
The CRC’s current goal is to further deepen the knowledge of the (patho-) physiology of the tubular system and the renal interstitium, with a focus on developing new diagnostic and therapeutic strategies.
RTG 2174: Neurobiology of social and emotional dysfunctions
Mental health as an essential prerequisite for a high quality of life, performance, and social integration is explored at UR as well. The main objective of the Research Training Group (RTG) 2174 Neurobiology of social and emotional dysfunctions (external link, opens in a new window) is to investigate the neurobiological mechanisms underlying mental disorders, such as anxiety disorders and major depression using appropriate laboratory animal models of impaired social interactions and emotionality.
PhD students are involved in translational research projects performed on molecular, genetic, epigenetic, cellular and systemic levels, and bridges three faculties and several UR institutes with the aim to contribute to the development of new treatment options.
Unique: The Archaea Center
A unique feature at UR’s Institute of Microbiology is the Archaea Center, founded in 1990:
It holds the largest collection of Archaea species in the world (external link, opens in a new window).
#notabene
#talktime
#illustratedscience
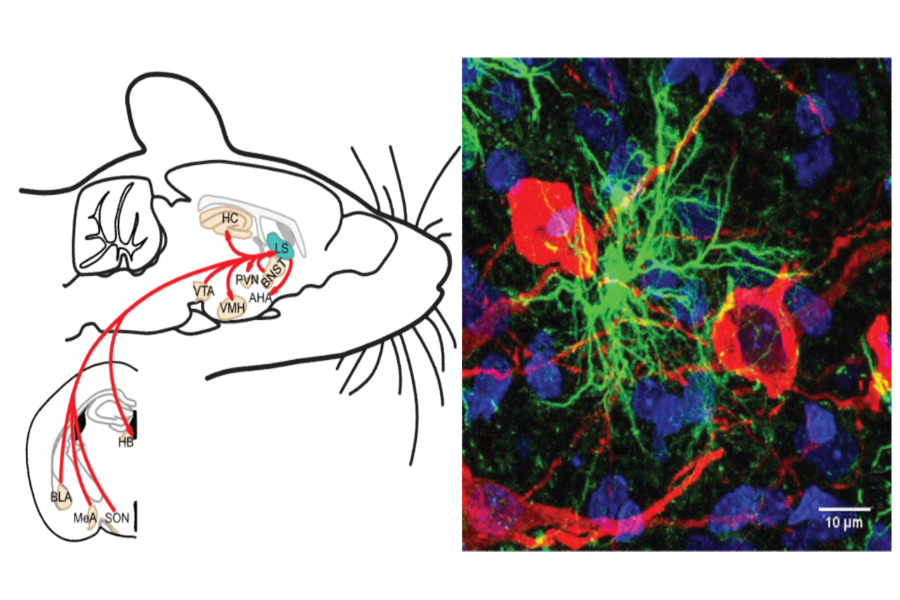 Courtesy of Inga Neumann © RTG 2174 Neurobiology of Socio-Emotional Dysfunctions, Carl-Philipp Meinung, PhD Thesis, 2021
Courtesy of Inga Neumann © RTG 2174 Neurobiology of Socio-Emotional Dysfunctions, Carl-Philipp Meinung, PhD Thesis, 2021 Complex interconnections between neurons regulate social and emotional behavior under physiological and pathological conditions: In addition to neurons producing oxytocin (red), brain astrocytes (green), for example in the hypothalamus, are playing an important role in the development of psychopathologies











