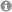nanofibers
 We develop a variety of nanomaterial-based systems including nanofibers. Electrospun nanofibers have been demonstrated by Antje Baeumner and her colleague, Margaret Frey from the Dept. of Fiber Science at Cornell University to be promising nanomaterials for bioanalytical sensors. Nanofibers can be created bearing diverse surface chemistries ranging from hydrophilic to hydrophobic or have amphoteric characteristics. They may bear functional groups, are biocompatible, non-fouling, and are capable to present biologically active molecules such as biotin on their surface. The nanofibers provide an immense surface-to-volume ratio and are therefore ideal components for integration into microfluidic devices or for paper-based microfluidics and lateral-flow assays. The Baeumner team investigates nanofibers for separation of analytes, immobilization of biorecognition elements, as detectors and also as mixing components. Dr. Nongnoot Wongkaew spearheads the development of conductive nanofibers in the institute.
We develop a variety of nanomaterial-based systems including nanofibers. Electrospun nanofibers have been demonstrated by Antje Baeumner and her colleague, Margaret Frey from the Dept. of Fiber Science at Cornell University to be promising nanomaterials for bioanalytical sensors. Nanofibers can be created bearing diverse surface chemistries ranging from hydrophilic to hydrophobic or have amphoteric characteristics. They may bear functional groups, are biocompatible, non-fouling, and are capable to present biologically active molecules such as biotin on their surface. The nanofibers provide an immense surface-to-volume ratio and are therefore ideal components for integration into microfluidic devices or for paper-based microfluidics and lateral-flow assays. The Baeumner team investigates nanofibers for separation of analytes, immobilization of biorecognition elements, as detectors and also as mixing components. Dr. Nongnoot Wongkaew spearheads the development of conductive nanofibers in the institute.
For example:
- Perju, A.T., Baeumner, A.J., Wongkaew, N., “Freestanding 3D-interconnected carbon nanofibers as high-performance transducers in miniaturized electrochemical sensors” Microchimica Acta (2022), 189, 424, https://doi.org/10.1007/s00604-022-05492-2
- Wongkaew, N., Simsek, M., Griesche, C., Baeumner, A.J. “Functional nanomaterials and nanostructures enhancing biosensors and lab-on-a-chip performances: recent progress, applications and future perspective” (2019) Chemical Reviews, 19(1), 120-194, https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.chemrev.8b00172
- Wongkaew, N., Simsek, M., Arumugam, P., Behrent, A., Berchmans, S. and Baeumner, A.J., “A Robust Strategy Enabling Addressable Porous 3D Carbon-based Functional Nanomaterials in Miniaturized Systems” Nanoscale (2019) 11, 3674 - 3680, https://doi.org/10.1039/C8NR09232J
- Yurova, N., Danchuk, A., Mobarez, S., Wongkaew, N., Rusanova, T., Baeumner, A.J., Duerkop, A. “”Functional Electrospun Nanofibers for Multimodal Sensitive Detection of Biogenic Amines in Food via a Simple Dipstick Assay“ Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, (2018) 410:1111-1121, DOI: 10.1007/s00216-017-0696-9
- Buchner, M., Ngoensawat, U., Schenck, M., Fenzl, C., Wongkaew, N., Matlock-Colangelo, L., Hirsch, T., Duerkop, A., Baeumner, A.J. “Embedded Nanolamps in Electrospun Nanofibers Enabling Online Monitoring and Ratiometric Measurements”, Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2017, DOI: 10.1039/C7TC03251J
- Matlock-Colangelo, L.E. , Colangelo, N.W., Fenzl, C., Frey, M.W., Baeumner, A.J. “Passive mixing capabilities of Micro- and Nanofibers when used in microfluidic systems” Sensors 2016, 16(8), 1238, DOI: 10.3390/s16081238
- Matlock-Colangelo, L.E., Coon, B., Pitner, C.L., Frey, M.W., Baeumner, A.J. “Functionalized electrospun poly(vinyl alcohol) nanofibers for on-chip concentration of E. coli cells” Analytical and Bioanalytical Chemistry, 408(5), 1327-1334 (2016), DOI: 10.1007/s00216-015-9112-5
- Reinholt, S.; Sonnenfeldt, A.; Naik, A.; Frey, M.; Baeumner, A.J “Developing new materials for paper-based diagnostics using electrospun nanofibers” Anal. Bioanal. Chem. vol. 406 (14) pp. 3297-3304 (2014), DOI. 10.1007/s00216-013-7372-5
- Li, D., Frey, F. W., Baeumner, A. J. ”Electrospun polylactic acid nanofiber membranes as substrates for biosensor assemblies” Journal of Membrane Science (2006), 279(1-2), 354-363, DOI: 10.1016/j.memsci.2005.12.036